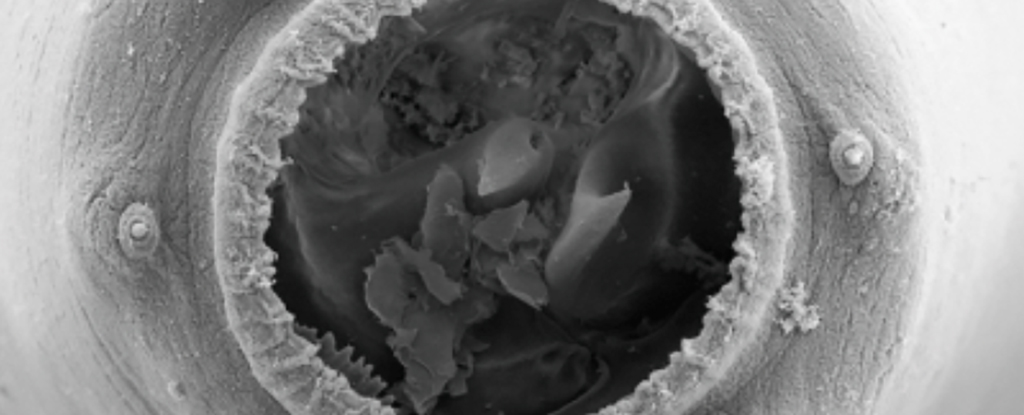
One thing fairly monstrous occurs to the nematode Allodiplogaster sudhausi when lowered to snacking on boring previous fungus. Scientists have found it develops a large mouth and feasts on different worms, together with these from its circle of relatives.
This new type has been named the teratostomatous morph, with “teras” being an historic Greek phrase for monster. Two different mouth formations have been beforehand described in this sort of worm, making this shape-shift quantity three.
The group behind the analysis, from the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Germany, Indiana College within the US, and the Forestry and Forest Merchandise Analysis Institute in Japan, thinks the massive mouth might be a response to emphasize.
Different nematodes (or roundworms) have been proven to develop mouths and eat one another when given sure diets, which prompted the research into A. sudhausi to get a better have a look at this fascinating and barely scary course of.
“To look at potential adjustments in mouth-form plasticity of A. sudhausi, we cultured these worms on a group of bacterial, fungal and nematode diets,” the researchers write of their paper.
“Remarkably, we discovered three distinct grownup mouth-forms when A. sudhausi was grown on Escherichia coli OP50 micro organism, C. elegans N2 worms, and Penicillium camemberti fungi.”
Utilizing genetic evaluation, the researchers have been capable of affirm this morphing capacity is linked to the worm having a second full copy of its total genome, one thing referred to as complete genome duplication. The additional copies of genes give the nematode the additional flexibility to rework itself.
The group zoomed in on one specific gene and its copy, Asu-sul-2-A/B, figuring out that these sequences managed the formation of the totally different mouths – together with the newly found third one.
Whereas additional research goes to be wanted to determine how and why A. sudhausi goes into cannibal mode, the researchers assume that it is a stress response to overcrowding and hunger. Opening up vast and indiscriminately snacking on something would give the worm a bonus in crowded environments or when meals is scarce.
Having the ability to adapt to altering circumstances and environments – technically known as developmental plasticity on this research – is clearly essential for animals eager to get forward, and for brand new transformations being attainable.
“In abstract, the invention of an extra mouth morph related to cannibalistic habits helps the significance of developmental plasticity as a serious driver of morphological and behavioral diversification,” write the researchers.
The analysis hasn’t but been peer reviewed however might be discovered on the preprint server bioRxiv.