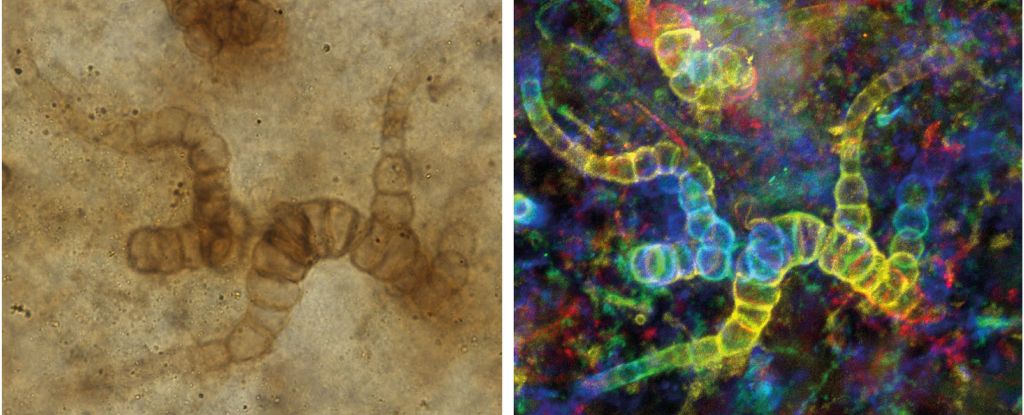
A detailed have a look at a mixture of outdated and newly found fossils signifies that an historical species of photosynthesizing bacterium was among the many first of its type to make its dwelling on dry land greater than 400 million years in the past.
Traits of a microbe named Langiella scourfieldii place it right into a class of cyanobacteria that may have lived, and thrived, amongst a number of the first crops to develop on land, in addition to in our bodies of freshwater and scorching springs as related species nonetheless do at this time.
“With the 3D reconstructions, we had been capable of see proof of branching, which is a attribute of Hapalosiphonacean cyanobacteria,” says paleobiologist Christine Strullu-Derrien of the Nationwide Historical past Museum within the UK.
“That is thrilling as a result of it signifies that these are the earliest cyanobacteria of this sort discovered on land.”
The invention was made in flakes of rock representing the world’s earliest recognized preserved terrestrial ecosystem, the Rhynie cherts in Scotland. Whereas a variety of life kinds have been recognized within the 407 million 12 months outdated fossil beds, the position of cyanobacteria hasn’t been clear.
Also called blue-green algae (despite the fact that they don’t seem to be really algae), cyanobacteria are marvelous issues. They’re fairly essential to life as we all know it at this time, having performed a key position in altering Earth into the hospitable atmosphere it’s at this time, some 2.4 billion years in the past. As they started to proliferate in Earth’s waters, they pumped the air filled with oxygen in what’s generally known as the Nice Oxidation Occasion.
Whether or not you take into account this a superb factor or a foul factor relies upon the place you might be in Earth’s historical past. From our completely satisfied, present, oxygen-breathing perspective, it is nice. For all the opposite life that had tailored to Earth in low-oxygen situations, it was fairly devastating. Mass extinction-levels of devastating.
However cyanobacteria, which will be discovered thriving all over the world at this time, did not care. The photosynthetic microbes simply stored on preserving on, inserting themselves into no matter ecological circumstances would take them.
As a result of they’re thought to have originated in freshwater environments, cyanobacteria are assumed to have made the leap from soggy circumstances to life on land fairly simply and early.
However simply the way it carved out a spot for itself is harder to determine. The brand new outcomes are an necessary piece of the puzzle.
“Cyanobacteria within the Early Devonian performed the identical position that they do at this time,” Strullu-Derien says.
“Some organisms use them for meals, however they’re additionally necessary for photosynthesis. We now have learnt that they had been already current when crops first started colonizing land and will have even competed with them for house.”
Langiella scourfieldii was first found in 1959, however the specimens had been troublesome to make out. Since then, nevertheless, extra specimens have been found, permitting the researchers to conduct a extra thorough investigation.
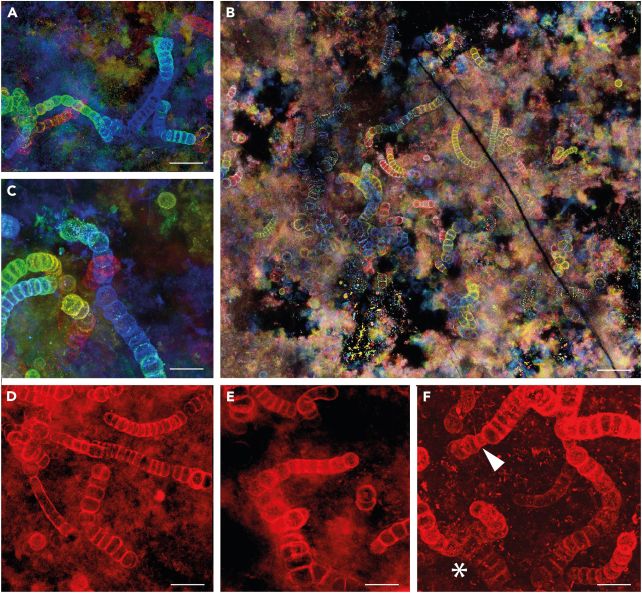
They used super-resolution microscopy and 3D reconstruction on new samples of Langiella scourfieldii to work out the way it grew.

They discovered proof of a structural attribute generally known as true branching, which is when micro organism rising collectively in a line typically double up, leading to one other line branching out. This, the group says, represents proof that the micro organism inhabited the moist land that ringed scorching springs.
Along with different proof, akin to molecular clock analyses, and samples akin to a billion-year-old branching specimen found in Africa a couple of years in the past, the outcomes recommend that cyanobacteria have a way more intricate evolutionary historical past than is preserved within the fossil file, the researchers say.
“Regardless of the emergence of embryophytes as each rivals for house and vitamins and new structural components in ecosystems of accelerating spatial complexity, cyanobacteria continued to thrive each inside Rhynie scorching springs and in adjoining wetlands as they do at this time in comparable terrestrial environments,” they write.
“In a position to colonize quickly, nostocalean cyanobacteria thrived in flooded surfaces with sedimented plant particles.”
The paper has been revealed in iScience.