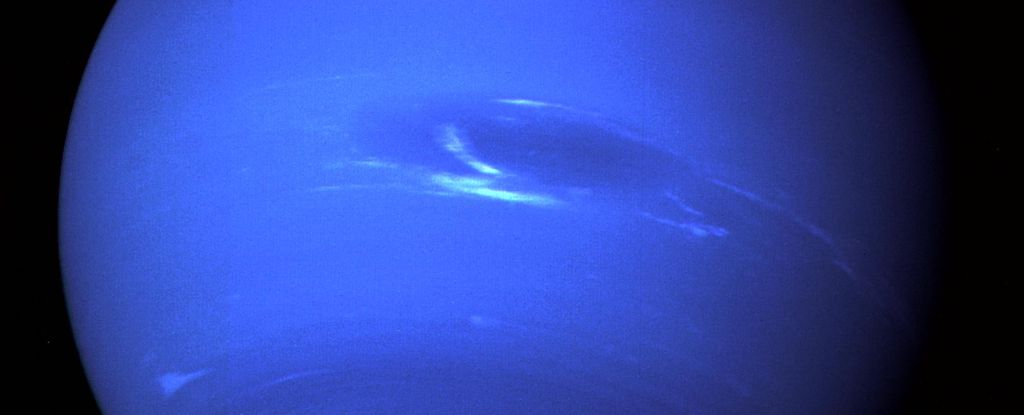
Neptune has experienced a strange event. The pale streaks that usually adorn Neptune’s blue atmosphere are all but gone.
Images from 1994, when Hubble began documenting Neptune for the first, prove that this isn’t a first. The fluctuations also seem linked to another periodic change – the 11-year activity of the Solar Cycle.
Given Neptune is from the Sun – about 4.5 billion kilometers, or just over 30 times the average distance between Earth and the Sun – this revelation has astronomers both surprised and intrigued.
Recent changes have been dramatic. In 2019, mid-latitude clouds began to fade. By 2020, the appearance of the planet was cloudless.
Even four years after, the images taken this past June show that the clouds haven’t recovered to their previous levels.” Erandi Chavez, astronomerHarvard University who led the research at UC Berkeley.
This is a very exciting and unexpected event, particularly since Neptune’s previous low cloud activity period was not as dramatic or prolonged.
Neptune is one of the Solar System’s most distant major planets. Understanding or being well educatedEarth’s nearest neighbors. The information we have indicates that a You can also find out more aboutYou can also find out more about the following: DynamicProcesses drive atmosphere We don’t quite understand.
Even though studying atmospheric trends from a distance is limited, it can be done. Chavez and colleagues focused on data collected by Hubble since 1994, by Keck Observatory since 2002, and by Lick Observatory between 2018 and 2019.
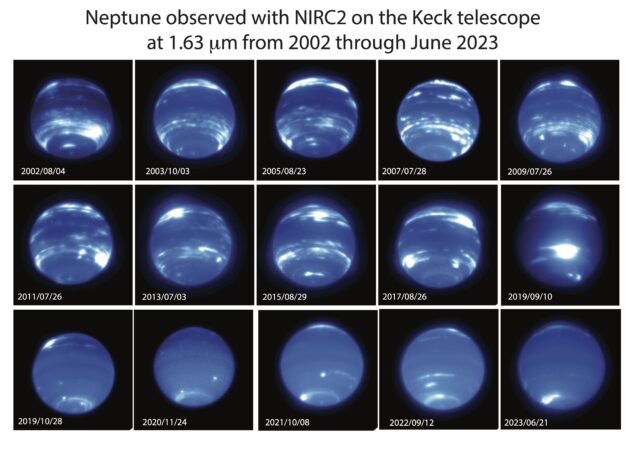
These combined datasets showed that the amount and frequency of clouds on Neptune fluctuates around 11-year cycles. This seems to be in sync with solar activity.
The magnetic field of the Sun reverses its polarity approximately every 11 years. This is marked by an increase in intensity. flares, Coronal mass ejectionsThe Sun’s polarities are switched, causing the Sun to grow. When the poles swap places, the Sun gets bigger Quieter for a whileBefore accelerating again to another solar maximum.
The Sun’s ultraviolet radiation increases in intensity as it approaches its maximum, irradiating our Solar System. The 29-year study shows that clouds appear around 2 years following the start of UV irradiation. Cloud cover on Neptune has a positive relationship with the planet’s brightness. Albedo – that’s the amount of sunlight it reflects.
These data are the most convincing evidence to date that Neptune cloud cover is correlated with the Sun cycle. says astronomer Imke de Pater of UC Berkeley.
Our findings support the idea that UV rays from the Sun, when they are strong enough, could trigger a photochemical process that creates Neptune’s cloud.
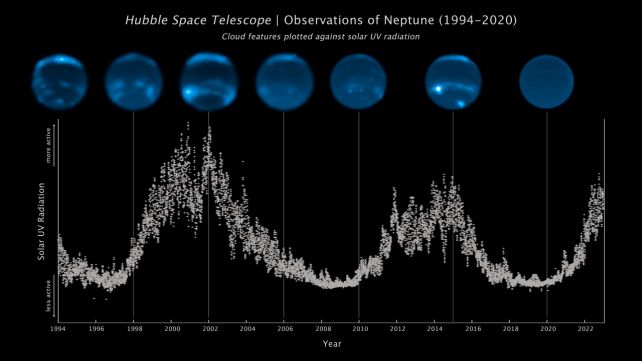
The team’s analysis of 2.5 solar cycles shows that Neptune’s albedo and cloud cover peaked in 2002. Previous studyAfter a brief rise, the cloud cover and albedo dropped to a low point in 2007. The cloud cover and albedo then climbed to a new peak in 2015 before falling again. The two recent solar maxima In 2001 and 2015, the events took place.
Scientists will need to crunch data to determine what these photochemical processes are. As an example, a UV interaction could cause clouds to darken, and not lighten, as this would reduce albedo. Storms can also occur from Deep within Neptune would be unrelated to photochemically-induced clouds, which represents a complication.
We have ongoing observations and new Erkenntnisse. Data from the James Webb Space Telescope. Both agree with the findings of the team heading into the next maximum solar, which is predicted to be in 2025.
“We’ve seen more clouds on the latest images, especially at northern latitudes. We also saw higher altitudes as we expected. Increase in the number of people observing this phenomenonIn the solar UV flux for the past 2 years, de Pater says.
It would be better to send an e-mail. Neptune to be studied up close by spacecraft. We’ll just have to do with what we can.
The research was published in Icarus.