In sediment samples from deep inside the ocean, scientists have recognized a mysterious and distinctive new species of marine micro organism that advances our understanding of deep-sea circumstances and microbiology typically.
A staff in China grew the micro organism within the lab utilizing sediment from a chilly seep, a particular puddle of nutrient-rich liquid and dirt method down on the ocean flooring.
Named Poriferisphaera hetertotrophicis by the analysis staff, it belongs to a phylum of micro organism that is not properly studied, although it is discovered everywhere in the world, from lakes to soils, and performs a vital half in recycling carbon and nitrogen.
“Most Planctomycetes micro organism have been remoted utilizing progress media which are nutritionally poor,” says microbiologist Rikuan Zheng from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences.
“So we wished to see if utilizing a nutrient-rich medium would make it attainable to tradition and additional characterize members of this poorly understood household.”
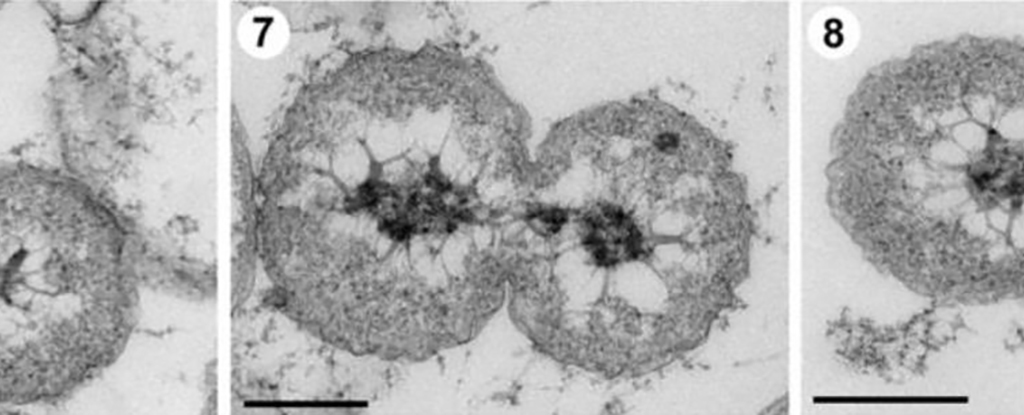
Zheng and staff’s novel method within the lab simulated deep-sea circumstances. The novel P. hetertotrophicis micro organism, a pressure labeled ZRK32, grew quicker than different cultured micro organism and multiplied another way than different related strains.
The budding mechanism, the place the mother or father cells develop buds that then change into their offspring, hasn’t been seen earlier than in Planctomycetes. It is maybe an indication of the extra uncommon circumstances that this pressure of micro organism lives in.
The brand new species additionally seems to work together with varieties of nitrogen – and the nitrogen cycle – in a brand new method, and it lives alongside a particular kind of bacteria-hugging virus (a bacteriophage) that helps its nitrogen processing.
All this performs into scientists’ understanding of the chemical processes taking place deep beneath the ocean floor.
“Our analyses point out that pressure ZRK32 is a novel species, which grows greatest in nutrient-rich media and releases a bacteriophage within the presence of nitrogen,” says microbiologist Chaomin Solar from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences.
“This phage-ZRK32 is a continual bacteriophage that lives inside its host with out killing it.”
Bacteriophages are vital to the nitrogen cycle too, similar to the micro organism that they coexist with. Future analysis might have a look at how phage-ZRK32 interacts with different strains of Planctomycetes and what the results are on the ocean atmosphere.
Contemplating Planctomycetes micro organism are so ubiquitous, comparatively little is thought about them in deep-sea environments – a information hole that the brand new examine and the newly recognized micro organism species assist to fill.
“Our findings present a novel perception into nitrogen metabolism in Planctomycetes micro organism and an appropriate mannequin to review the interactions between Planctomycetes and viruses,” says Solar.
The analysis has been revealed in eLife.