Tremendous mud suspended within the environment might have performed a big function within the extinction of dinosaurs in any case.
It is largely accepted that round 66 million years in the past, an area rock bigger than Mount Everest smashed into what’s right this moment the coast of Mexico, setting off a cascade of catastrophes that in the end killed three-quarters of life on Earth, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs.
However the finer particulars of how this all unfolded are nonetheless up for debate.
Now, scientists have cracked open a geological ‘black field’ that means the asteroid affect created a plume of fantastic mud which blocked daylight, cooled the Earth, shut down photosynthesis, and destroyed the meals chain.
Initially proposed as a mechanism in 1980 by the geologists who uncovered the primary indicators of the mighty affect, the speculation was dominated out within the early 2000s as a result of rock samples from this period did not include sufficient fantastic mud to trigger a worldwide winter.
Nevertheless, most earlier research had been primarily based on one-centimeter-thick layers of sediment from the Cretaceous-Paleogene interval. (Not a variety of filth to sink one’s enamel into.)
This new research analyzed 40 samples of sediment taken from a a lot richer, 1.3-metre-deep deposit in Tanis, North Dakota. This website is 3,000 kilometers (about 1,900 miles) north of the Chicxulub asteroid crater, however it gives a singular snapshot of how plumes of mud, soot, and particles unfold within the years post-impact.
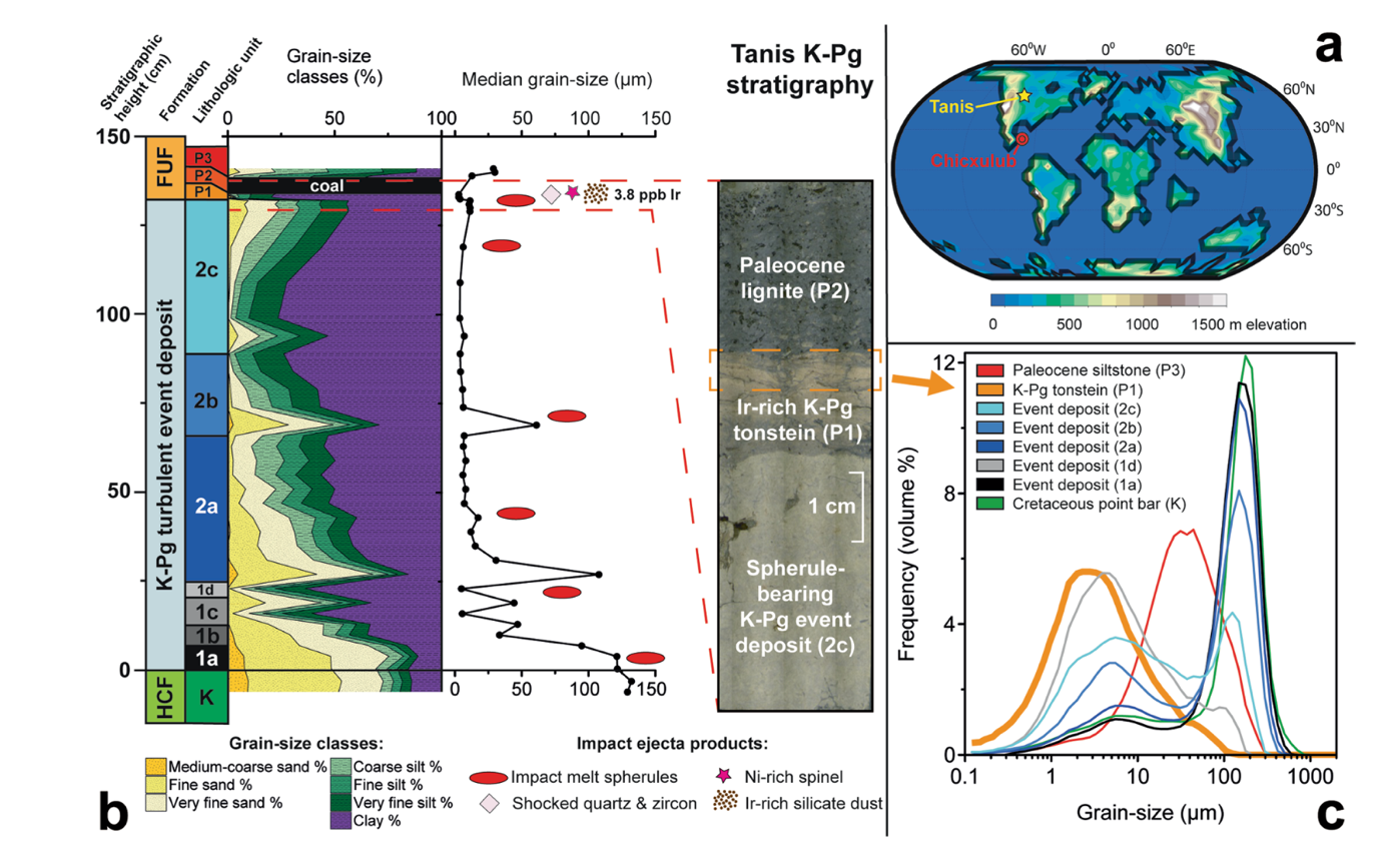
Bigger particles scatter mild at smaller angles than finer particles, so utilizing a laser, the researchers had been capable of decide how a lot of every pattern was made up of fantastic silicate mud within the 0.8 to eight micrometer vary.
“[We found] a bigger contribution of fantastic mud… than beforehand appreciated,” wrote the researchers.
Utilizing pc modeling, the researchers found that this fantastic mud – created when the asteroid hit the Earth and pulverized the rock beneath – was “probably the most deadly” of the particles launched when the ten to 15-kilometer-wide meteorite collided with Earth.
They discovered that prime ranges of mud within the environment would have created a worldwide darkness lasting virtually two years, which might have made it inconceivable for vegetation to photosynthesize.
With out vegetation, the whole meals chain would have collapsed. The highest predators – like Tyrannosaurus rex – hunted prey that trusted vegetation as a part of their weight loss program.
This mud might have stayed suspended within the air for as much as 15 years, inflicting a 15°C fall in world temperatures and inducing a “photosynthetic shut-down for nearly two years post-impact” by blocking daylight, the researchers wrote.
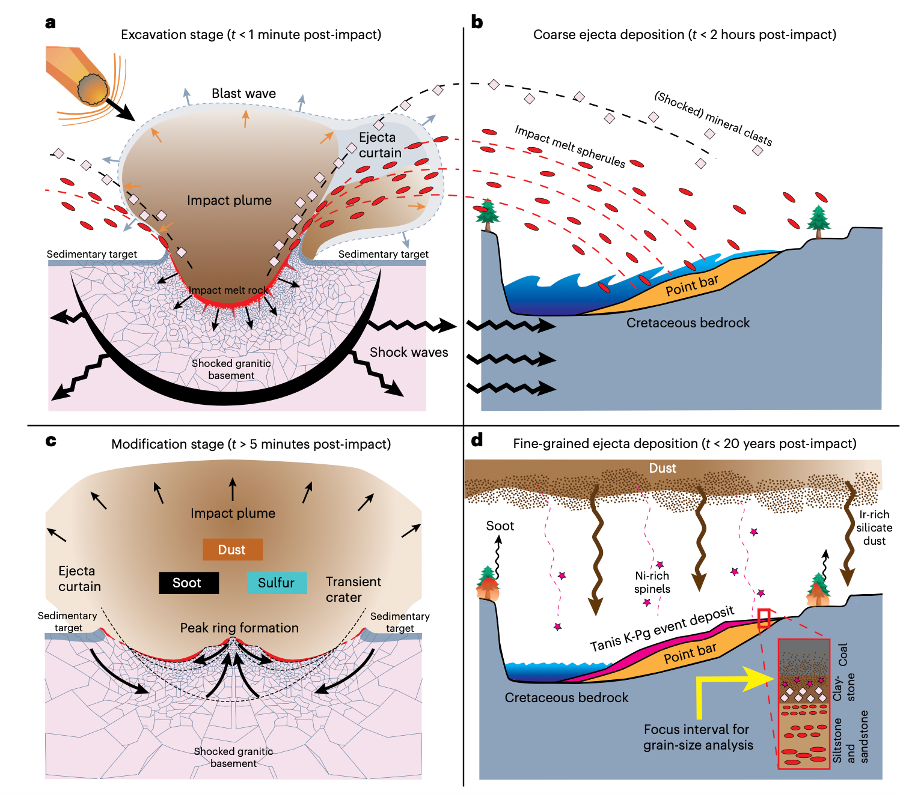
The shock of the collision additionally would have vaporized rock and produced sulfur-bearing gasses that type into small particles excessive within the environment. And the extraordinary warmth produced by the asteroid’s affect would have sparked large-scale wildfires, sending massive quantities of soot and ash into the sky.
But based on the researcher’s outcomes, it was the fantastic silicates moderately than materials like sulfur particles that had been primarily chargeable for the prolonged planetary winter.

“We discover that the worldwide darkness and extended loss within the planet’s photosynthetic exercise happen solely within the silicate mud state of affairs, as much as almost 1.7 years (620 days) after affect,” the researchers wrote.
“This constitutes a sufficiently lengthy timescale to pose extreme challenges for each terrestrial and marine habitats.”
These animals and vegetation that weren’t tailored or couldn’t adapt to reside in the dead of night and chilly would have met their demise. Wildlife with versatile diets, habitats, and existence would have had a better probability of survival.
The Chicxulub asteroid affect additionally unleashed a mega-tsunami 1.5-kilometres tall that hit each continent on Earth, and set off seismic exercise 50,000 instances extra highly effective than the 2004 Sumatra earthquake.
This paper was revealed in Nature Geoscience.


