Particle accelerators are vastly helpful in scientific analysis, however – like the Giant Hadron Collider (LHC) – normally take up huge quantities of room. A outstanding new system developed on the College of Texas in Austin may change this.
In experiments, researchers had been ready to make use of their particle accelerator to generate an electron beam with an vitality of 10 billion electron volts (10 GeV) in a chamber measuring simply 10 centimeters (4 inches).
The entire instrument measures 20 meters (66 toes) from finish to finish. Compared, different particle accelerators that may generate 10 GeV beams are some 3 kilometers (nearly 2 miles) in size – about 150 occasions as lengthy.
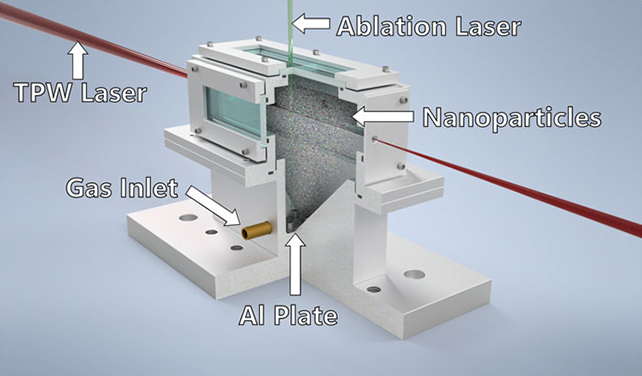
Key to decreasing the scale of the system so considerably was combining high-energy, ultra-short laser pulses with helium gasoline dusted with aluminum nanoparticles.
These particles increase the vitality of electrons stripped from the nanoparticles by the laser, that are pushed to the perimeters of the laser the place they journey the laser-induced plasma waves like surfers on the wake of a ship on a lake.
Whereas the energy of those waves would usually be overwhelming – in the identical approach that jet skis overpower the waves left behind by boats – the nanoparticles supply extra stability and permit the system to be shrunk down.
“In our accelerator, the equal of jet skis are nanoparticles that launch electrons at simply the correct level and simply the correct time, so they’re all sitting there within the wave,” says physicist Bjorn Hegelich, from the College of Texas at Austin.
“We get much more electrons into the wave when and the place we wish them to be, fairly than statistically distributed over the entire interplay, and that is our secret sauce.”
Any such particle accelerator, utilizing lasers to generate plasma waves, is known as a wakefield laser accelerator. The crew says their superior model might be helpful in learning semiconductors, in testing tools for area, and in growing most cancers therapies.
All that is potential due to the way in which these devices speed up electrons (therefore the identify) to excessive speeds, producing energetic waves of electromagnetic radiation equivalent to X-rays that might be used to picture molecular-scale processes.
The researchers are trying ahead to growing the system additional, however there’s nonetheless so much concerning the interactions between electrons, lasers, and plasma that we do not absolutely perceive. In different phrases, there are many thrilling scientific discoveries forward.
“At the moment, we shouldn’t have a passable mannequin or experimental rationalization for the technology of such excessive electron energies,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.
“Numerous theoretical situations are actually below investigation and, if related, would be the topic of future publications.”
The analysis has been revealed in Matter and Radiation at Extremes.