For greater than 300 million years, mammals of all sizes and styles have flourished right here on Earth.
Right now, this extremely profitable class of animal exists in almost each main habitat on land, having endured by way of large local weather fluctuations and a number of other mass extinctions.
It is exhausting to think about a world with out them. But a brand new examine led by researchers from the College of Bristol suggests the shifting of continents will finally spell doom for any and all warmblooded, milk-producing creatures.
Current fashions predict Earth’s greenhouse gasoline impact may attain a tipping level that renders a lot of the planet “uninhabitable to mammalian life” when the subsequent supercontinent – a landmass some name Pangea Ultima – kinds within the coming 250 million years or so.
“The formation and decay of Pangea Ultima will restrict and… in the end finish terrestrial mammalian habitability on Earth by exceeding their heat thermal tolerances, billions of years sooner than beforehand hypothesized,” the researchers behind the mannequin write.
At present, consultants perceive little or no about what occurs to Earth’s local weather when its continents smoosh collectively into one large landmass, a world-changing occasion that has occurred on greater than few events in our planet’s historical past.
Earth’s final supercontinent, referred to as Pangea, happened roughly 310 million years in the past and is the one which scientists know most about.
Utilizing Pangea as a case examine, a world workforce of researchers from the US, UK, China, and Switzerland tried to foretell what is going to occur to Earth’s local weather throughout the formation of the subsequent supercontinent.
Their outcomes counsel that within the distant future, issues are going to grow to be quite a bit hotter… like, unbearably scorching.
Not solely will the Solar emit round 2.5 % extra radiation, the formation of a supercontinent will drastically alter the worldwide local weather system, probably drying out large swathes of land and trapping extra carbon dioxide within the ambiance.
Throughout the time of the primary Pangea, between 334 million years in the past and 255 million years in the past, atmospheric carbon dioxide ranges rose from about 200 components per million to as excessive as 2,100 ppm. This created excessive temperatures round 10 °C greater than the present-day international imply.
To place that in perspective, present atmospheric carbon dioxide ranges sit round 416 ppm relative to preindustrial ranges.
If, sooner or later, atmospheric carbon dioxide spike previous 560 ppm as soon as once more, even for only a century, it may result in a mass extinction occasion on par with the ‘Large 5’.
Sadly, fashions counsel that is more likely to occur when Pangea Ultima kinds, as plate tectonics create local weather feedbacks and altered climate methods. If much less contemporary water is carried to inside areas, for example, it may dry out forests and switch inland carbon sinks into carbon faucets.
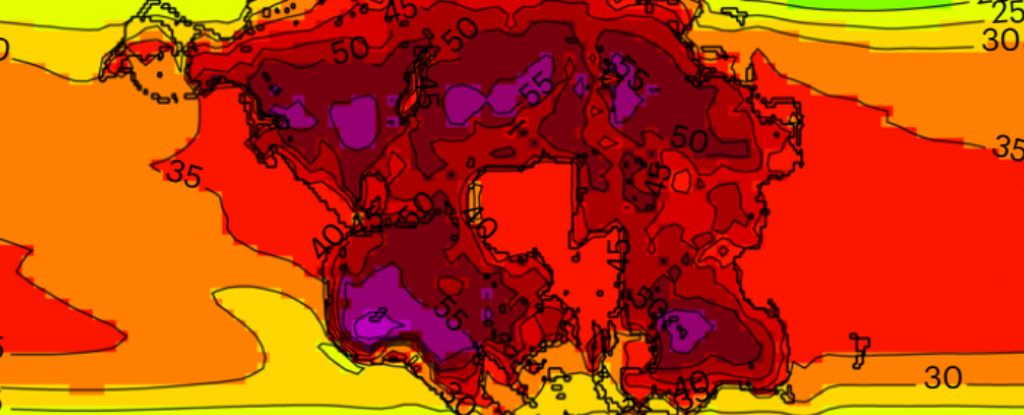
Modeling the worst case state of affairs, researchers predict that Pangea Ultima may lead to a heat month imply temperature of 46.5 °C (115.7 °F).
Judging by at the moment’s data of crucial warmth stress amongst mammals, these temperatures will possible be prohibitive for the overwhelming majority of recognized species.
“At 280 ppm, a lot of the tropics grow to be uninhabitable,” the researchers clarify, “and by 1,120 ppm this extends by way of the mid to excessive latitudes”
In reality, at 1,120 ppm, fashions counsel not more than 8 % of Pangea Ultima will proceed to assist mammalian life. At this drastic stage, just some high-latitude refuges can be left, as will be seen within the picture under.
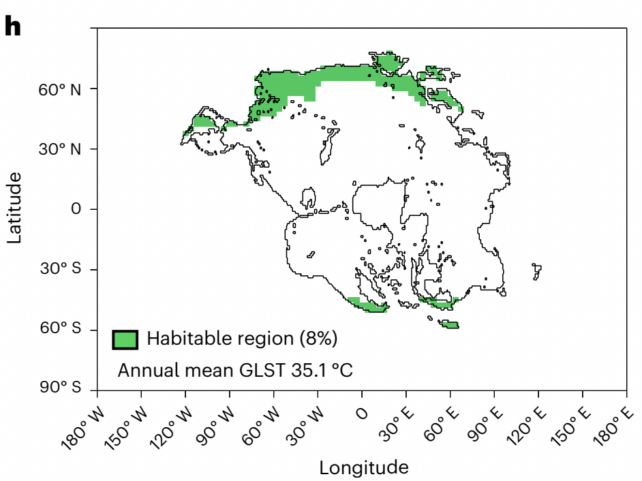
Burrowing nocturnal rodents would possibly nonetheless survive on this area, as may “extremely specialised migratory mammals“.
However even mammals that journey from habitat to habitat will face perilous circumstances as continent-wide deserts kind all through Pangea Ultima, making journey by way of these arid sections largely ‘impractical’.
“Though we can’t low cost evolutionary adaptation to warmth and chilly stress, latest research have proven that mammalian thermotolerance higher limits are conserved by way of geologic time and haven’t elevated throughout previous fast or slower warming occasions,” the researchers write.
Provided that historic context, there’s little likelihood that mammals will evolve quick sufficient to deal with Earth’s subsequent supercontinent.
All good issues should come to an finish.
The examine was revealed in Nature Geoscience.