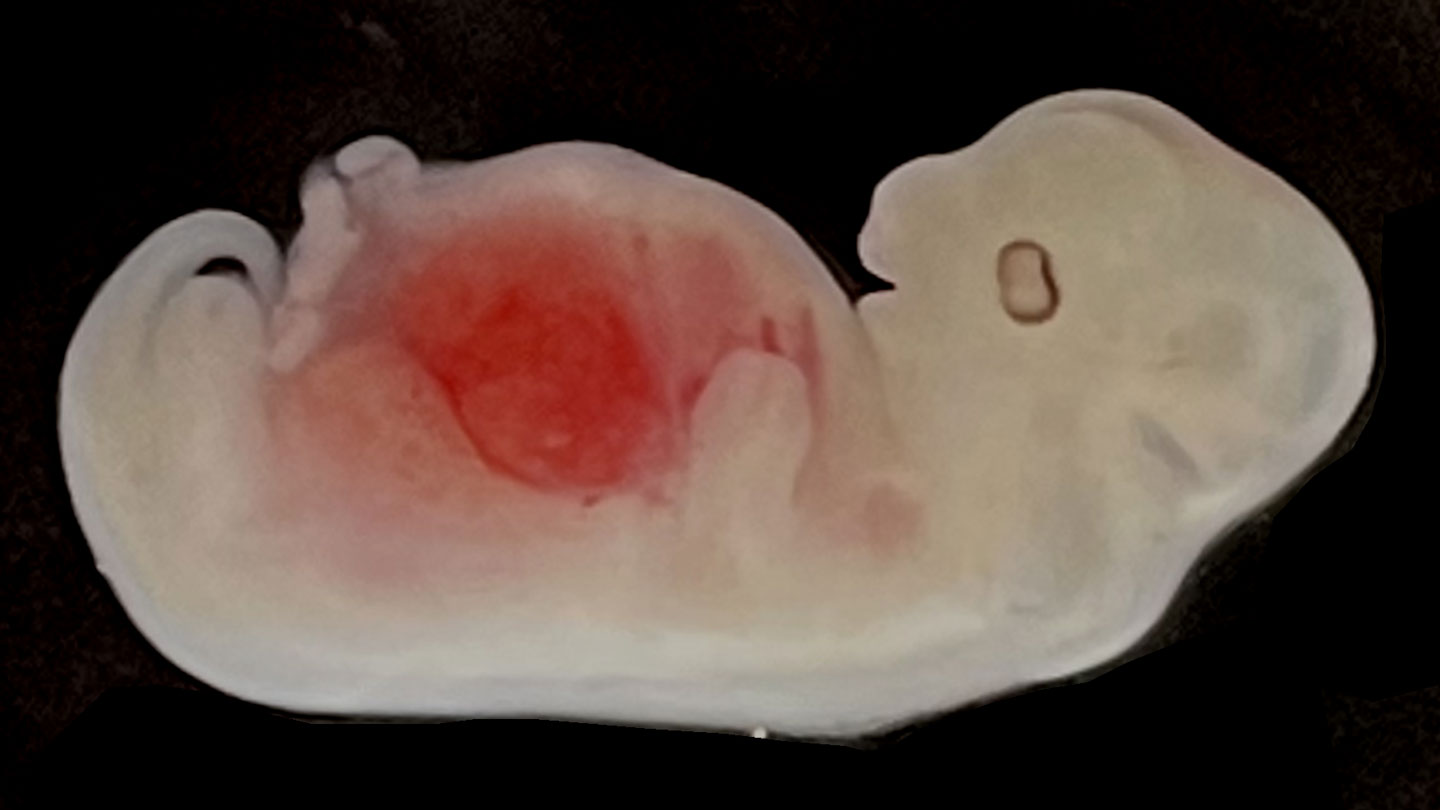
Scientists have efficiently grown kidneys made from principally human cells inside pig embryos — taking researchers one more step down the lengthy street towards producing viable human organs for transplant.
The outcomes, reported September 7 in Cell Stem Cell, mark the primary time a strong humanized organ, one with each human and animal cells, has been grown inside one other species.
“It is a appreciable progress in human-animal chimerism,” says Tao Tan, a cell biologist on the Kunming College of Science and Expertise in China, who helped create the primary chimeric human-monkey embryo in 2021 however was not concerned within the present research.
In america alone, greater than 100,000 individuals at the moment sit on an organ transplant ready listing. A overwhelming majority of these individuals want a kidney transplant. To satisfy this demand for life-saving organ transplants, scientists have been pursuing new strategies to develop organs and tissues in animals (SN: 1/26/17).
Advances in the previous couple of years embrace rising rat organs in mice (and vice versa) and humanized skeletal muscle and endothelial tissue in pigs. However vital hurdles stay, due partially to how difficult it’s for human cells to thrive inside a overseas host. Human induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs, which perform as a type of “starter package” for rising many sorts of human tissue, usually die when launched into animals as a result of the species’ cells have totally different physiological wants.
Stem cell biologist Liangxue Lai, of the Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Well being in China, and his staff spent greater than 5 years refining their strategies to reinforce the human stem cells’ survivability.
Whereas the pig embryos have been nonetheless simply single cells, the staff used the gene-editing software CRISPR/Cas9 to edit out two genes needed for kidney improvement. That created a distinct segment by which the human iPSCs, as soon as injected into the house, might turn into kidney cells. The human stem cells have been additionally tweaked to have particularly lively genes that dampen apoptosis, or cell dying, to maintain the cells alive lengthy sufficient to realize a foothold and start forming the kidney.
Greater than 1,800 embryos have been then transferred into surrogate sows, of which 5 have been harvested for research throughout the first 28 days. All 5 had regular kidneys in keeping with their degree of improvement, and the organs contained 50 % to 60 % human-derived cells. That’s the best share of human cells but noticed in any organ grown inside a pig, Tan says. Given extra time, there’s no indication that the kidneys wouldn’t proceed to develop and develop usually, presumably with the human cells more and more edging out the pig cells, the researchers say.
The research is “an vital and attention-grabbing step,” says Massimo Mangiola, a transplant immunologist at New York College Langone Well being who was not concerned within the analysis. Nevertheless it’s nonetheless a few years out from totally useful xenotransplants, he notes.
Whereas the stem cells did differentiate into a number of cell varieties, together with kidney tubular cells and developmental tissue, the human kidney has greater than 70 distinctive cell varieties that scientists might want to recapitulate. And till researchers can create an organ that’s 100% human, it’s seemingly that such transplants will immediate rejection.
As well as, a couple of iPSCs erroneously differentiated into neural cells within the brains and spinal cords of the embryos. Mangiola says that the cells seem like random, in contrast to the kidney cells, making him assume they’re not more likely to lead to animals with human brains — which might create an moral quandary.
To keep away from such moral points, Lai says that shifting ahead the staff will knock out genes that orchestrate the stem cells’ differentiation into neurons — in addition to into germline cells, eggs and sperm, which cross genetic data on to offspring. The staff can be pursuing rising different human organ precursors in pigs as effectively, together with the center and pancreas.
“We really feel that we have now completed a milestone within the discipline, however that is solely step one, and plenty of challenges stay,” Lai says. “We’re optimistic that with effort and time we could possibly overcome these challenges too.”