Recordings from the interior of MarsThe results of this most accurate measurement are confusing.
Mars’ rotation increases by 4 milliarcseconds per year, according to data collected from the InSight Lander. That’s a very small amount – shortening the length of a Mars day by just a fraction of a millisecond every Martian year – but the reason for it is not immediately apparent.
This discovery may help us understand Mars and its evolution in the past. The current forerunning hypotheses explaining the acceleration are long-term trends – such as accumulating material at the polar ice caps – and interior dynamics.
“It’s really cool to be able to get this latest measurement – and so precisely,” Bruce Banerdt is a geophysicist who specializes in planetary scienceJet Propulsion Laboratory, NASA. I’ve worked for decades to get a geophysical observatory like InSight on Mars, and the results of this mission make it all worthwhile.
InSight has been retired because its power is no longer available. In December 2022I was able to get a hold of the data that it collected over its four-year operation. It has given scientists plenty to think about. IIn just four years of operation, the rover has revolutionized our understanding. Its seismic recording revealed not just the surface but also the depths of the planet. Mars’ interior structureBut the Composition of its liquid core. ongoing geodynamic activity.
Although the previous study has been insightful, the data used in this new study did not come from seismic recordings. Instead, it came from radio communications between InSight Rotation and the Interior Structure Experiment. RISENASA’s Instruments and. Deep Space NetworkEarth.
Scientists were able to measure the rotation of Mars by measuring the subtle variations in radio wave frequency as Earth and Mars rotated.
The team discovered the small acceleration based on the 900 Martian Days of Insight communication with Earth. This has to do, in some way, with the redistribution or mass of Mars. On Earth, however, the opposite is happening: Long-term trends indicate that Earth’s population has been decreasing. The rotation has slowed downThis is due to a brake effect that has been applied by MoonThe oceans are towed by the Earth’s gravity, which redistributes Earth mass.
Mars has no oceans. So, something else is happening. Scientists must do a deeper investigation to find the cause of this acceleration.
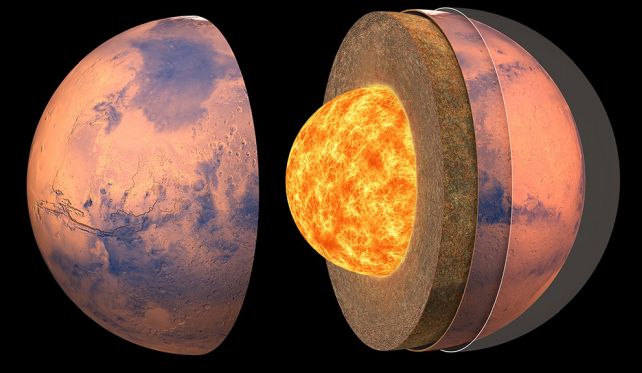
RISE data allowed the team refine measurements of the Martian Core by measuring a wobble known as nutationFluids moving about can cause a fluid.
Seismic data suggests that the core of Mars lies between 1,780The following are some examples of how to get started: Radius of 1,830 km (1,137 miles)., which is rather large – more than half the planetary radius of 3,390 kilometers. Seismic analysis Please see below for further informationCore density between 6.2 and 6.3 grams per cubic millimeter.
RISE data are in perfect agreement with the measurements. They give a core radius between 1,835 and 1,835 kilometers, as well as a density range of 5,9 to 6,3 grams per cubic centimeter. The nutation of the planet suggests that the density is not evenly distributed. Future analysis will need to probe the density variations within the core.
It’s an historic experiment.” says astronomer Sebastien Le MaistreThe Royal Observatory of Belgium
We have invested a great deal of time and effort in preparing for this experiment and anticipating the discoveries. But despite this, we were still surprised along the way – and it’s not over, since RISE still has a lot to reveal about Mars.”
The research has appeared in Nature.


